September 14, 2021
Carriage Bolts - Everything You Need to Know
Carriage Bolts: Everything you need to know
Bolts are one of the three main designs of threaded fasteners, and are used to connect unthreaded objects when combined with a nut. Designed in the early 1800's, carriage bolts were used for carriages and carriage wheels. You don't see many carriages on the roads these days, but these fasteners are still a popular choice for wood and metal projects.
Carriage bolts are recognizable by their round, wide,
domed heads and square neck. This design allows carriage bolts to be self-locking when inserted into a pre-drilled
hole. Carriage bolts may be fully threaded, or partially threaded to suit your project needs.

What are carriage bolts used for?
Many people choose to use carriage bolts in their projects due to security, ease of use, and the bolt's ability to support a large amount of weight.
The smooth domed head of carriage bolts is designed to be flush with the surface it is installed in. This lowers the possibility of snagging or catching other materials on the bolt. The carriage bolt also offers security due to the fact that it can only be removed from the nut side of the bolt. There are no grooves or indentations in the head of the bolt to allow a tool to gain purchase from the non nut secured side.
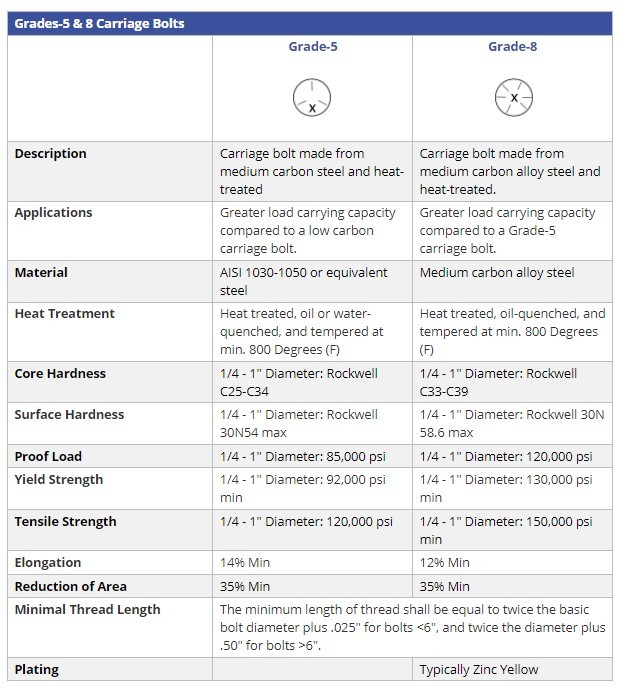
Though carriage bolts can only be utilized with pre-drilled holes, they are easy to install and usually only need the use of a single tool. The square neck of the bolt prevents it from rotating while the nut is being tightened. Many choose the carriage bolt due to its ability to support a large amount of weight when installed correctly. A grade 5 carriage bolt made from medium carbon steel and heat-treated, with a diameter of ¼” to 1”, has a tensile strength of 120,000 psi and a proof load of 85,000 psi.
What are the Different Grades and Materials for Carriage Bolts?
Choosing the right carriage bolt is essential to ensure the durability and longevity of your project. Carriage bolts are produced in a multitude of materials, finishes, and grades that need to be considered to meet your specific needs.
Bolt Grades
Grades of bolts are based on common measurements such as proof load (an axial tensile load which the product must stand without evidence of any permanent set), tensile strength (the resistance of a material to breaking under tension), yield strength (the stress at which a specific amount of deformation is produced), and Rockwell hardness (how resistant a metal object is to penetration and permanent deformation from another material). These categories can also help you determine what your bolt is made of. Bolt grades can be categorized as inch or metric and are usually marked on the head of the bolt for quick identification.
Bolt Materials
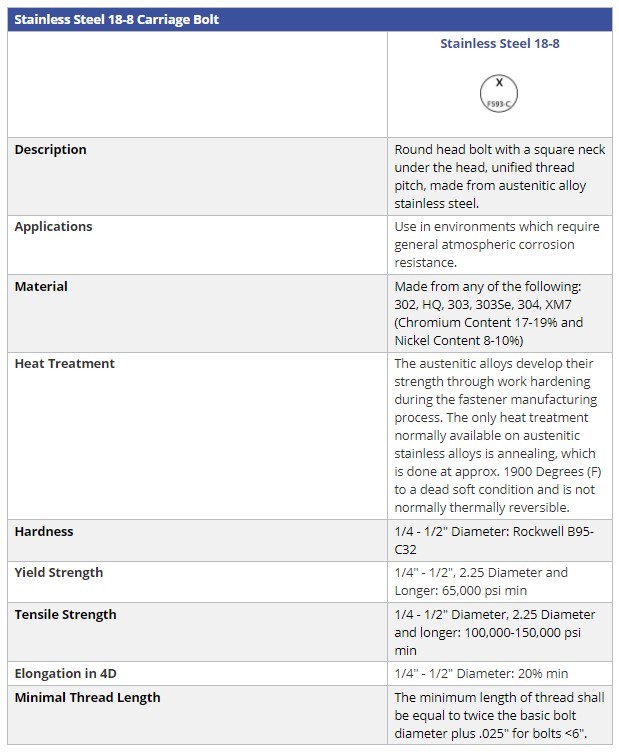
The main concern with choosing the correct material for your carriage bolt is preventing corrosion. Making sure you prevent corrosion on your project can help mitigate safety risks and repair costs. Stainless steel, galvanized, and zinc plated materials are among the most popular options for carriage bolts due to their beneficial qualities.
Stainless steel fasteners are a popular choice because they offer resistance to corrosion and do not rust or tarnish. Stainless steel is also resistant to internal and external hydrogen embrittlement, and are self repairing due to a natural layer of oxidation that forms on the material when exposed to oxygen. This material also endures very high and low temperatures giving it lasting value in many environments including underwater. Stainless steel is low maintenance, resistant to scratching, and easy to clean.
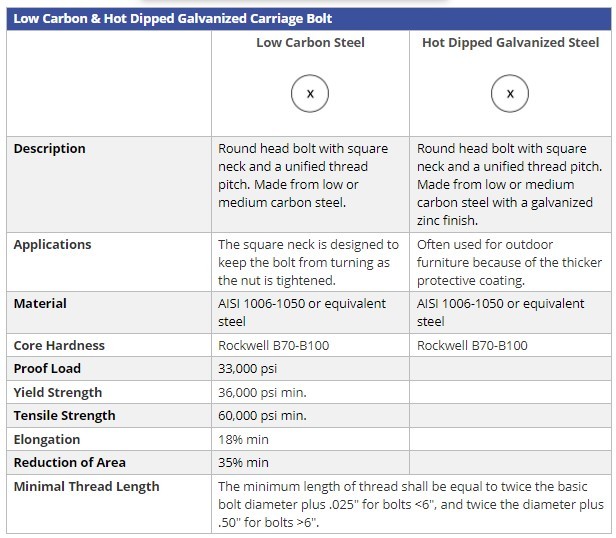
Steel is the most common base for mechanical fasteners, but steel is susceptible to corrosion from oxidation so steel fasteners often have a zinc coating applied to prevent corrosion. This coating is primarily applied through electroplating or through hot dip galvanization. Zinc electroplated fasteners are popular due to their cost effectiveness, and ability to ward off the oxidation that leads to rust and corrosion. Zinc coatings are also flexible, have a high temperature tolerance, and are environmentally friendly. Adding a layer of zinc also helps add lubricity to the threads of the fastener, and surface hardness to the base metal.
Hot dipped galvanized zinc coating is another popular option. This process applies a zinc coating to the fasteners to provide durability, complete coverage, and a longer service life. The hot dip galvanizing process is denser than other zinc coatings and produces a strong bond between the zinc and base steel. Due to the process of hot dipping using molten zinc, a more complete and consistent coverage of the fastener is achieved. The lifetime of galvanized coatings depends on how thick the coating is; the thicker the coating the longer it will take corrosion to penetrate to the steel. Hot dipped coatings will typically last around 65 years in mild rural atmospheres, and over 35 years in industrial atmospheres.
Why AFT Fasteners
AFT Fasteners has a proven history of helping our customers choose the right fasteners for their projects. Our knowledgeable staff can help make sure that you get the grades, materials, and options that will save you time and money. Contact us to learn more, or order carriage bolts easily online.